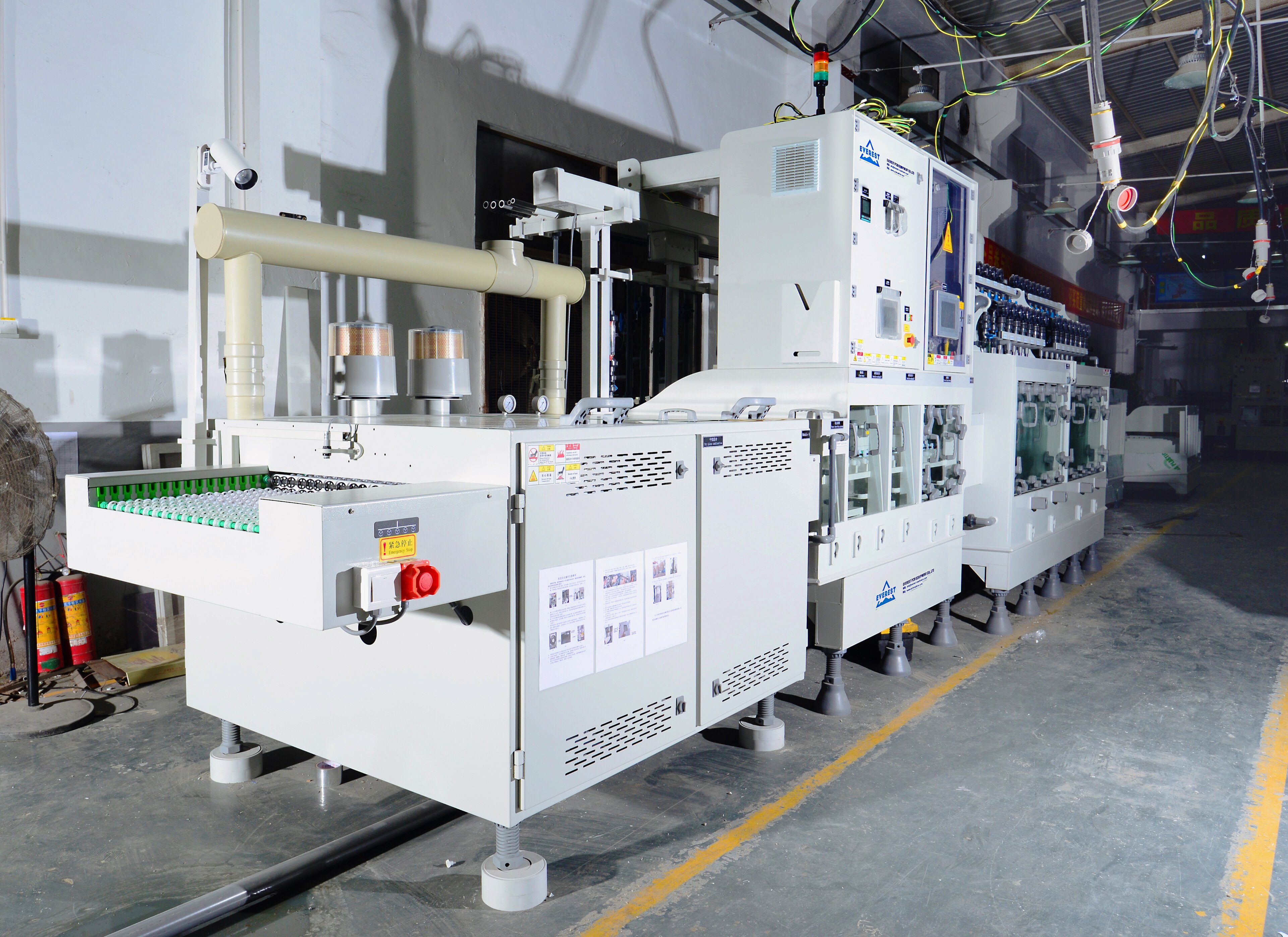
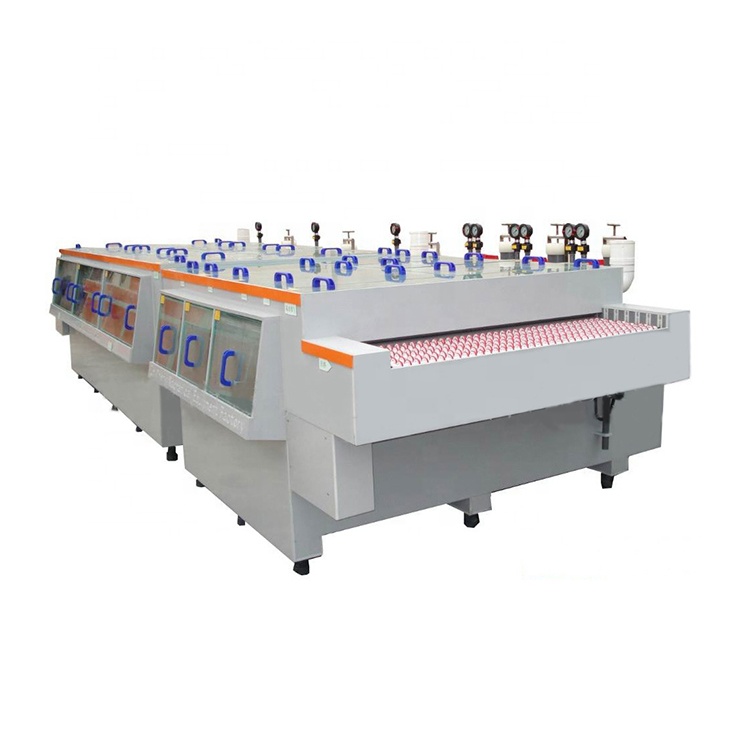
印刷电路板从光学板到显示电路图案的过程是一个相对复杂的物理和化学反应过程。本文分析了最后一步——;蚀刻。目前,印刷电路板(PCB)加工的典型工艺是;图案电镀”;也就是说,在铜箔部分上预镀一层铅锡防腐层,以保留在电路板的外层,即电路的图形部分,然后对铜箔的其余部分进行化学腐蚀,这被称为蚀刻。
蚀刻类型:
需要注意的是,蚀刻时板上有两层铜。在外层蚀刻过程中,只需要完全蚀刻一层铜,其余的将形成最终所需的电路。这种图案电镀的特点是镀铜层仅存在于铅锡耐腐蚀层下方。
另一种工艺是整个电路板镀上铜,感光膜外的部分只有锡或铅锡耐腐蚀层。此过程称为“;全板镀铜工艺”;与图案镀相比,全板镀铜的最大缺点是必须在板上的任何地方镀两次铜,并且在蚀刻过程中必须被腐蚀。因此,当线宽非常细时,会出现一系列问题。同时,侧面腐蚀会严重影响线条的均匀性。
在印刷电路板外电路的加工技术中,还有另一种方法,即使用感光膜代替金属涂层作为防腐层。这种方法与内层蚀刻工艺非常相似,可以参考内层制造工艺中的蚀刻。
目前,锡或铅锡是最常用的抗蚀剂层,用于氨蚀刻剂的蚀刻过程。氨蚀刻剂是一种广泛使用的化学溶液,与锡或铅锡没有化学反应。氨蚀刻剂主要是指氨水/氯化铵蚀刻液。
此外,氨水/硫酸铵蚀刻溶液也可以在市场上买到。硫酸盐基雕刻液中的铜在使用后可以通过电解分离,因此可以重复使用。由于其腐蚀速率低,在实际生产中通常很少见,但预计将用于无氯蚀刻。
有人试图使用硫酸过氧化氢作为蚀刻剂来蚀刻外部图案。由于经济和废液处理等诸多原因,该工艺尚未在商业意义上得到广泛应用。此外,硫酸过氧化氢不能用于蚀刻铅锡抗蚀层,而且该工艺不是生产PCB外层的主要方法,因此大多数人很少关注它。
蚀刻质量和预先存在的问题:
蚀刻质量的基本要求是完全去除除防腐层下的所有铜层,并且;这就是全部。严格来说,如果我们想准确地定义它,蚀刻质量必须包括线宽的一致性和侧面侵蚀的程度。由于目前腐蚀性溶液的固有特性,它不仅可以向下蚀刻,还可以左右蚀刻,因此侧面侵蚀几乎是不可避免的。
蚀刻参数中经常讨论侧面蚀刻问题。它被定义为侧面蚀刻宽度与蚀刻深度的比值,称为蚀刻因子。在印刷电路行业,它有着广泛的变化,从1:1到1:5。显然,小侧面蚀刻或低蚀刻因子是最令人满意的。
蚀刻设备的结构和不同成分的蚀刻溶液会对蚀刻因子或侧面蚀刻程度产生影响,或者乐观地说,它是可以控制的。使用一些添加剂可以降低侧面腐蚀程度。这些添加剂的化学成分通常是商业机密,其各自的开发人员不会向外界披露。
在许多方面,蚀刻的质量早在印刷电路板进入蚀刻机之前就已经存在了。因为印刷电路加工的各种过程或过程之间存在非常密切的内部联系,所以没有一个过程不受其他过程的影响,也不影响其他过程。许多被确定为蚀刻质量的问题实际上存在于之前的薄膜去除过程中,甚至更多。
对于外部图形的蚀刻工艺,许多问题最终反映在它身上,因为其;逆流”;图像比大多数PCB工艺更突出。同时,这也是因为蚀刻是从自涂层和光敏性开始的一系列工艺中的最后一步。之后,外部图案被成功转移。链接越多,出现问题的可能性就越大。这可以看作是印刷电路生产过程中一个非常特殊的方面。
从理论上讲,印刷电路进入蚀刻阶段后,在通过图案电镀加工印刷电路的过程中,理想的状态应该是:电镀后铜和锡或铜和铅锡的总厚度不应超过耐电镀感光膜的厚度,使电镀图案完全被电镀图案阻挡;墙壁”;然而,在实际生产中,世界各地印刷电路板的电镀图案比电镀后的感光图案厚得多。在电镀铜和铅锡的过程中,由于涂层高度超过感光膜,有水平积累的趋势,从而导致问题。覆盖在线路上方的锡或铅锡防腐层延伸到两侧;边缘”;,覆盖感光膜下的一小部分;边缘”;。
“;边缘”;由锡或铅锡形成的薄膜使得在去除薄膜时无法完全去除感光薄膜;残留胶水”;在“;边缘”;. “残留胶水”;或者“;我的电影”;留在“;边缘”;抗蚀剂的剥离将导致蚀刻不完全。线条形成“;铜根”;蚀刻后的两侧,线间距变窄,导致印刷板不符合甲方要求;他们的要求,甚至可能被拒绝。拒收将大大增加PCB的生产成本。
此外,在许多情况下,溶解是由于反应形成的。在印刷电路行业中,残留的薄膜和铜也可能积聚在腐蚀性溶液中,堵塞腐蚀性机器和耐酸泵的喷嘴,因此必须停机进行处理和清洗,这会影响工作效率。




 2021年11月9日
2021年11月9日