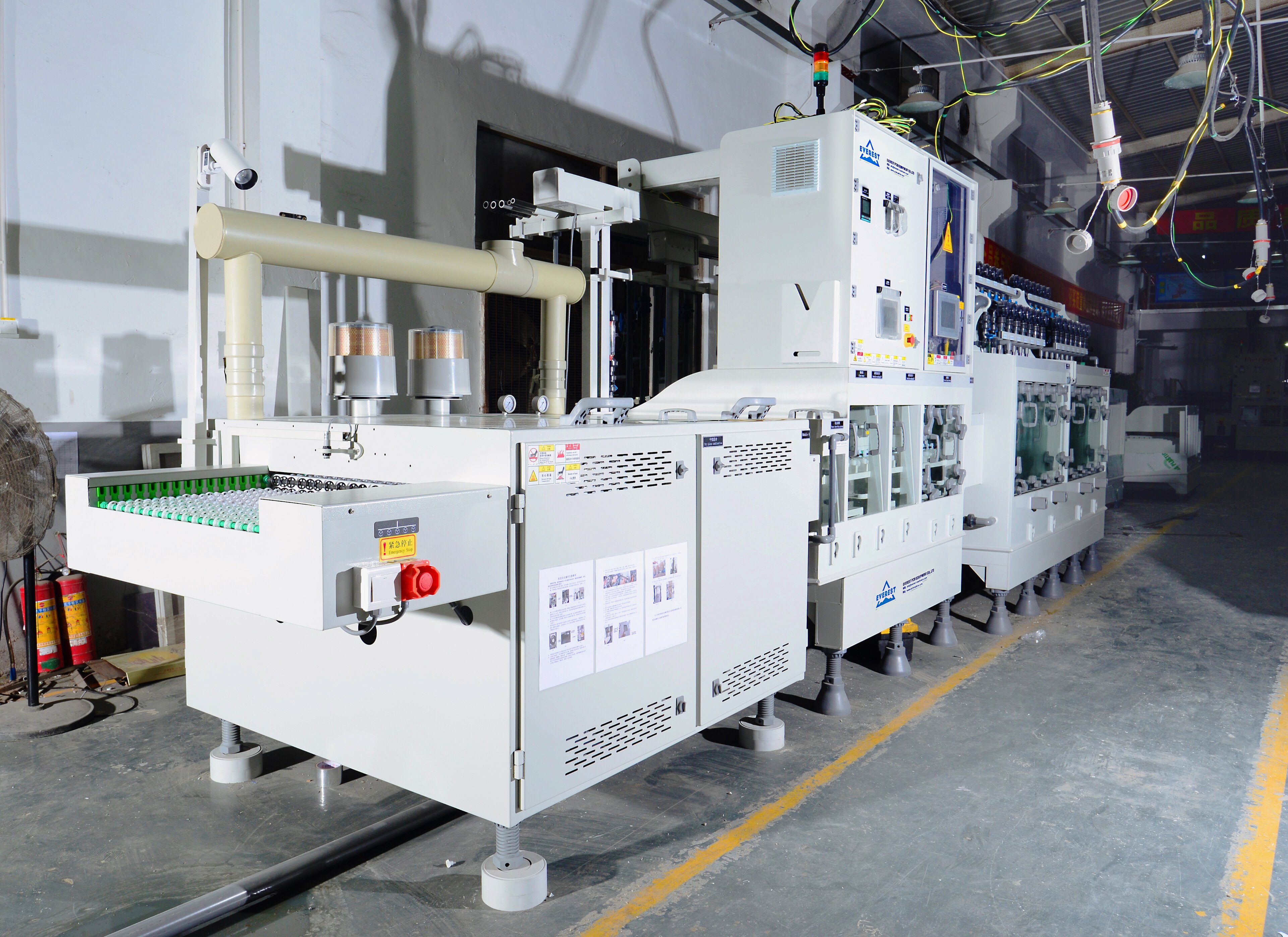
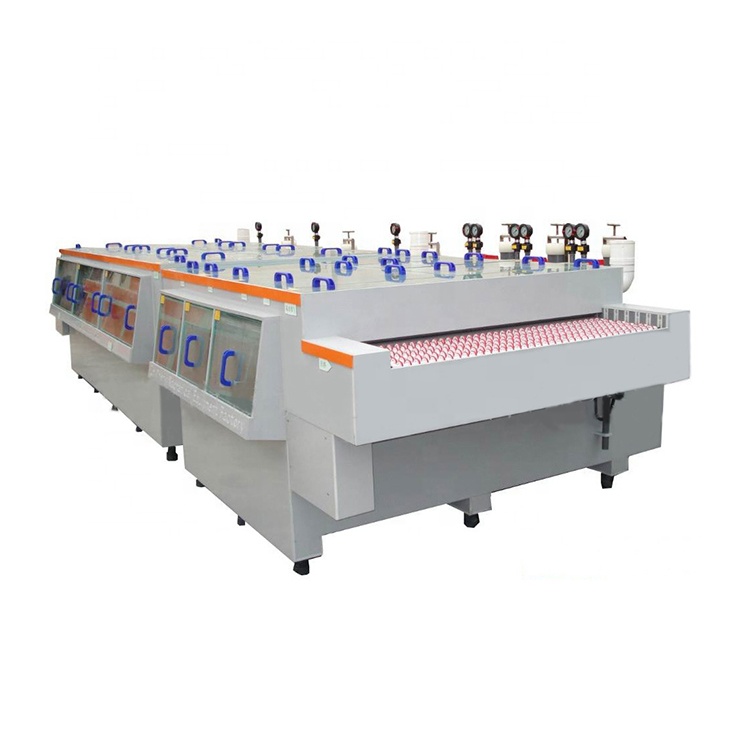
عملية لوحة الدائرة المطبوعة من اللوحة البصرية لعرض نمط الدائرة هي عملية تفاعل فيزيائية وكيميائية معقدة نسبيا. تحلل هذه الورقة الخطوة الأخيرة – الحفر. في الوقت الحاضر ، العملية النموذجية لمعالجة لوحة الدائرة المطبوعة (PCB) هي “ نمط طلاء” . أي ، يتم طلاء طبقة من طبقة الرصاص القصدير المضادة للتآكل مسبقا على جزء رقائق النحاس ليتم الاحتفاظ بها على الطبقة الخارجية من اللوحة ، أي الجزء الرسومي من الدائرة ، ثم يتم تآكل بقية رقائق النحاس كيميائيا ، والتي تسمى الحفر.
نوع الحفر:
تجدر الإشارة إلى أن هناك طبقتين من النحاس على اللوحة عند الحفر. في عملية حفر الطبقة الخارجية ، يجب حفر طبقة واحدة فقط من النحاس بالكامل ، وسيشكل الباقي الدائرة المطلوبة النهائية. يتميز هذا النوع من الطلاء الكهربائي النمطي بحقيقة أن طبقة الطلاء النحاسية موجودة فقط تحت طبقة الرصاص المقاومة للتآكل.
عملية أخرى هي أن اللوحة بأكملها مطلية بالنحاس ، والجزء الخارجي للفيلم الحساس للضوء هو فقط طبقة مقاومة للتآكل من القصدير أو القصدير الرصاصي. تسمى هذه العملية “ عملية طلاء النحاس كاملة” . مقارنة مع طلاء النمط ، أكبر عيب في طلاء النحاس على اللوحة بأكملها هو أنه يجب طلاء النحاس مرتين في كل مكان على اللوحة ، ويجب تآكلها أثناء الحفر. لذلك ، عندما يكون عرض الأسلاك دقيقًا جدًا ، ستحدث سلسلة من المشاكل. في نفس الوقت ، سيؤثر التآكل الجانبي بشكل خطير على توحيد الخطوط.
في تكنولوجيا معالجة الدائرة الخارجية لللوحة المطبوعة ، هناك طريقة أخرى ، وهي استخدام الفيلم الحساس للضوء بدلا من الطلاء المعدني كطبقة مضادة للتآكل. هذه الطريقة مشابهة جدا لعملية الحفر الطبقة الداخلية ، ويمكنك الرجوع إلى الحفر في عملية تصنيع الطبقة الداخلية.
في الوقت الحاضر ، القصدير أو القصدير الرصاصي هو طبقة المقاومة الأكثر شيوعًا ، والتي تستخدم في عملية حفر الأمونيا الحفر الأمونيا الحفر هو محلول كيميائي مستخدم على نطاق واسع ، ليس له تفاعل كيميائي مع القصدير أو القصدير الرصاصي. الحفر الأمونيا يشير أساسا إلى مياه الأمونيا / محلول الحفر كلوريد الأمونيا.
بالإضافة إلى ذلك ، يمكن شراء محلول الحفر في مياه الأمونيا / كبريتات الأمونيا في السوق. يمكن فصل النحاس في محلول النقش القائم على الكبريتات عن طريق التحليل الكهربائي بعد الاستخدام ، لذلك يمكن إعادة استخدامه. بسبب معدل التآكل المنخفض ، فإنه نادر بشكل عام في الإنتاج الفعلي ، ولكن من المتوقع استخدامه في الحفر الخالي من الكلور.
حاول شخص ما استخدام بيروكسيد الهيدروجين حمض الكبريتيك كحفر لحفر النمط الخارجي. بسبب العديد من الأسباب بما في ذلك الاقتصاد ومعالجة سائل النفايات ، لم تستخدم هذه العملية على نطاق واسع بالمعنى التجاري علاوة على ذلك ، لا يمكن استخدام بيروكسيد الهيدروجين حمض الكبريتيك لحفر طبقة مقاومة القصدير الرصاص ، وهذه العملية ليست الطريقة الرئيسية في إنتاج الطبقة الخارجية لثنائي الفينيل متعدد الكلور ، لذلك نادراً ما يولي معظم الناس اهتماماً لها.
جودة الحفر والمشاكل الموجودة مسبقاً:
المتطلبات الأساسية لجودة الحفر هي إزالة جميع طبقات النحاس بالكامل باستثناء طبقة مكافحة التآكل ، وهذا ’ كل شيء. بالتحديد ، إذا أردنا تعريفه بدقة ، يجب أن تتضمن جودة الحفر اتساق عرض الأسلاك ودرجة التآكل الجانبي. بسبب الخصائص المتأصلة في الحل التآكل الحالي ، يمكن أن يحفر ليس فقط للأسفل ولكن أيضًا الاتجاهات اليسرى واليمينة ، لذلك فإن التآكل الجانبي شبه حتمي.
غالبا ما يتم مناقشة مشكلة الحفر الجانبي في معايير الحفر. يتم تعريفه كنسبة عرض الحفر الجانبي لعمق الحفر ، والذي يسمى عامل الحفر. في صناعة الدوائر المطبوعة ، لديها مجموعة واسعة من التغييرات ، من 1: 1 إلى 1: 5. من الواضح أن الحفر الجانبي الصغير أو عامل الحفر المنخفض هو الأكثر رضا.
هيكل معدات الحفر وحل الحفر مع مكونات مختلفة سيكون له تأثير على عامل الحفر أو درجة الحفر الجانبية ، أو بكلمة متفائلة ، يمكن التحكم فيها. يمكن تقليل درجة التآكل الجانبي باستخدام بعض المضافات. المكونات الكيميائية لهذه المضافات هي عادة أسرار تجارية، ومطوريها لا يكشف عنها للعالم الخارجي.
في نواح كثيرة ، كانت جودة الحفر موجودة قبل فترة طويلة من دخول اللوحات المطبوعة إلى آلة الحفر. لأن هناك اتصال داخلي وثيق جدا بين مختلف العمليات أو عمليات معالجة الدائرة المطبوعة، لا توجد عملية لا تتأثر بعمليات أخرى ولا تؤثر على عمليات أخرى. العديد من المشاكل المحددة على أنها جودة الحفر كانت موجودة فعلا في العملية السابقة لإزالة الأفلام أو حتى أكثر.
بالنسبة لعملية الحفر للرسومات الخارجية ، تنعكس العديد من المشاكل أخيراً فيها لأنها “ تدفق عكسي” الصورة هي أكثر وضوحا من معظم عمليات PCB. وفي نفس الوقت، يعزى ذلك أيضًا إلى أن الحفر هو الخطوة الأخيرة في سلسلة طويلة من العمليات بدءاً من الطلاء الذاتي والحساسية الضوئية. بعد ذلك ، يتم نقل النمط الخارجي بنجاح. كلما زادت الروابط، كلما زادت احتمال المشاكل. يمكن اعتبار هذا جانبا خاصا جدا في عملية إنتاج الدائرة المطبوعة.
من الناحية النظرية ، بعد أن تدخل الدائرة المطبوعة مرحلة الحفر ، في عملية معالجة الدائرة المطبوعة عن طريق الطلاء الكهربائي النمط ، يجب أن تكون الحالة المثالية: يجب ألا يتجاوز سمك النحاس والقصدير أو النحاس والقصدير الرصاصي بعد الطلاء الكهربائي سمك الفيلم الحساس للضوء المقاوم للطلاء الكهربائي ، بحيث يتم حظر نمط الطلاء الكهربائي تمامًا بواسطة “ جدران” على جانبي الفيلم ومضمنة فيه. ومع ذلك ، في الإنتاج الحقيقي ، فإن نمط طلاء لوحات الدوائر المطبوعة في جميع أنحاء العالم سميك بكثير من نمط الحساسية للضوء بعد الطلاء الكهربائي. في عملية الطلاء الكهربائي للنحاس والقصدير الرصاصي ، لأن ارتفاع الطلاء يتجاوز الفيلم الحساس للضوء ، هناك اتجاه للتراكم الأفقي ، مما يؤدي إلى مشاكل. طبقة القصدير أو القصدير الرصاص المضادة للتآكل المغطاة فوق الخط تمتد إلى كلا الجانبين لتشكيل “ حافة” تغطي جزءًا صغيرًا من الفيلم الحساس للضوء تحت “ حافة”.
في “ حافة” يتكون من القصدير أو القصدير الرصاصي يجعل من المستحيل إزالة الفيلم الحساس للضوء بالكامل عند إزالة الفيلم ، مما يترك جزءًا صغيرًا من “ الغراء المتبقي” تحت “ حافة” . “ الغراء المتبقي” أو “ فيلم” يسار تحت “ حافة” من المقاومة سوف تسبب الحفر غير الكامل. شكل الخطوط “ جذور النحاس” على كلا الجانبين بعد الحفر ، مما يضيق المسافة بين الخطوط ، مما يسبب فشل اللوحة المطبوعة في تلبية الطرف A ’ متطلبات ويمكن حتى رفضها. الرفض سيزيد بشكل كبير من تكلفة إنتاج PCB.
بالإضافة إلى ذلك ، في العديد من الحالات ، يتم تشكيل الحل بسبب التفاعل. في صناعة الدوائر المطبوعة ، قد يتراكم الفيلم المتبقي والنحاس أيضًا في محلول التآكل ويحجب في فوهة الآلة المتآكلة والمضخة المقاومة للحمض ، لذلك يجب إغلاقها للعلاج والتنظيف ، مما يؤثر على كفاءة العمل.




 نوفمبر 09, 2021
نوفمبر 09, 2021